Placing Control Points
A control point is a specific point on the floor or wall of the site. It has to be marked clearly and assigned a unique identifier.
The following are recommendations for control points:
- Distribute control points evenly. Place them more than 5m apart from one another and, if possible, not in a straight line.
- Place control points at the beginning and end of each dataset.
- Include at least three control points per dataset.
- For automatic alignment without measured control points, neighboring datasets must have at least two control points in common in order to align the datasets to each other.
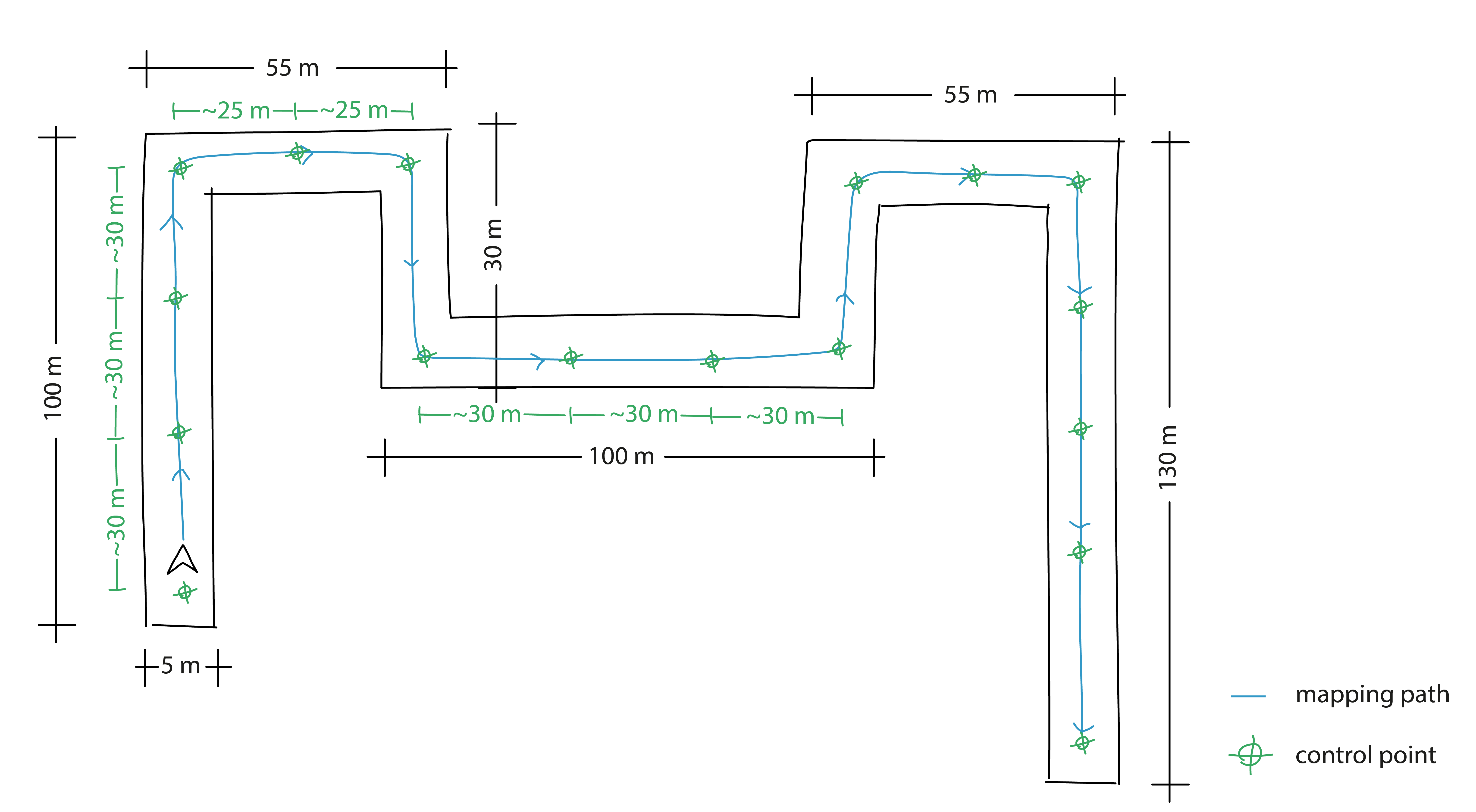
- To improve map accuracy, place control points in corners, at the ends of corridors, and measure them. Place one control point at every corner of a long corridor. Details depend on the building layout.
- Ground control points should be placed at least 50 cm from corners. One control point every 25m. Wall control points should be 160-180 cm high.
There is no fixed rule for how many control points to use within a dataset. It depends on the building layout and use case.
Measured Control Points: Improved Absolute Accuracy
When using measured control points to improve the absolute accuracy of the trajectory estimate, effective placement depends on the building layout. It is a tradeoff between how accurate the mapping results need to be and the time spent on placing and measuring the control points.
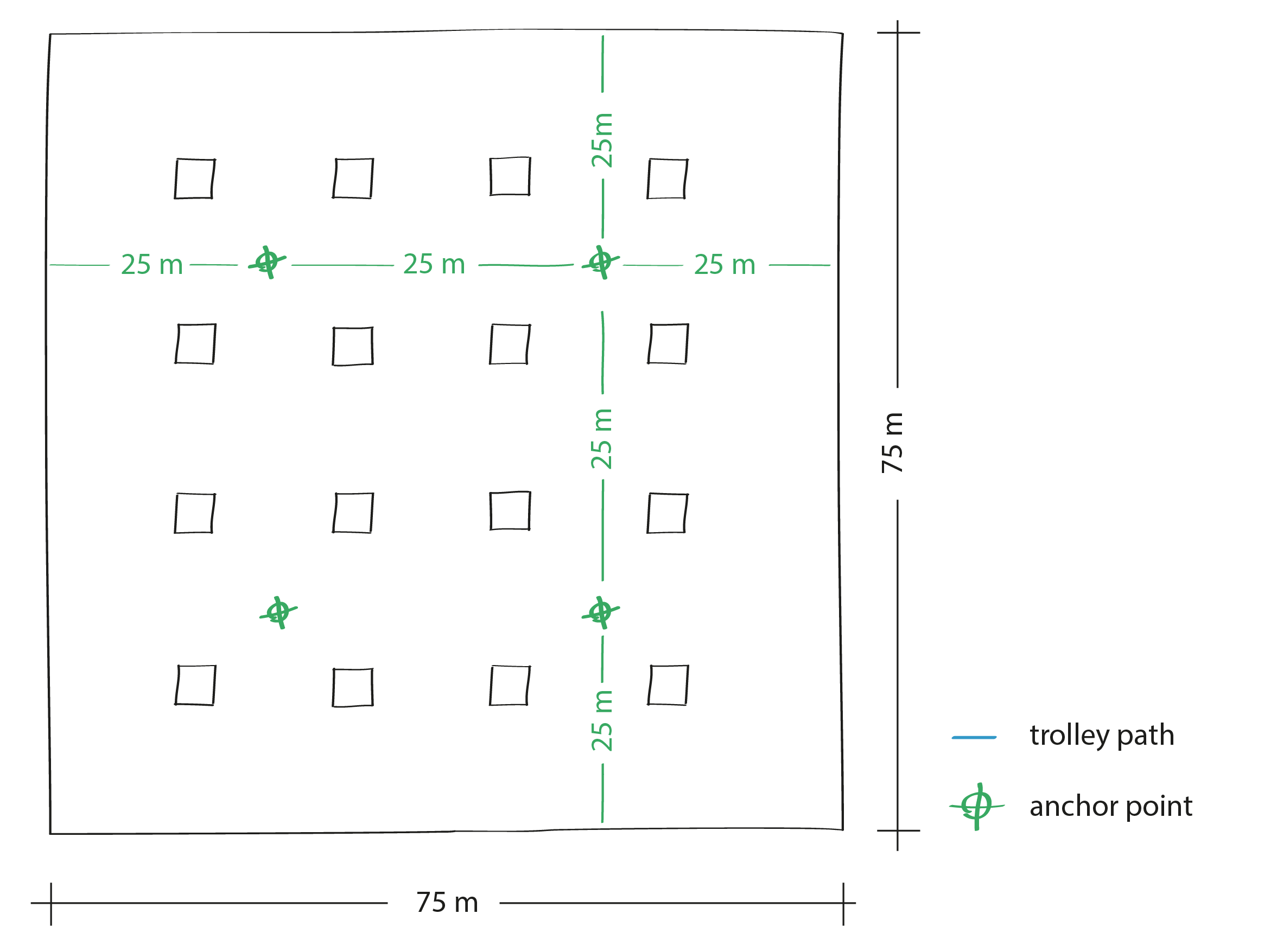
In this type of building layout, we advise placing control points every 25 meters of the device's trajectory, at every corner and the ends of corridors, for high map and point cloud accuracy.
We recommend uniformly distributing control points in both directions, every 25 meters, creating a two-dimensional grid of points.